Modifies a dataset x so that it shares sample summary statistics with
a target dataset x2.
Arguments
- x, x2
Numeric matrices or data frames. Each column contains observations on a different variable. Missing observations are not allowed.
get_stats(x2)sets the target summary statistics. Ifx2is missing thenset_statsis called withd = ncol(x)and any additional arguments supplied via.... This can be used to set target summary statistics (means, variances and/or correlations).- idempotent
A logical scalar. If
idempotent = TRUEthenmimic(x, x)returnsx, apart from a change ofclass. Ifidempotent = FALSEthen the returned dataset may be a rotated version of the original dataset, with the same summary statistics. See Details.- ...
Additional arguments to be passed to
set_stats.
Value
An object of class c("anscombe", "matrix", "array") with
plot and print methods. This returned
dataset has the following summary statistics in common with x2.
The sample means of each variable.
The sample variances of each variable.
The sample correlation matrix.
The estimated regression coefficients from least squares linear regressions of each variable on each other variable.
The target and new summary statistics are returned as attributes
old_stats and new_stats.
If x2 is supplied then it is returned as a attribute old_data.
Details
The input dataset x is modified by shifting, scaling and rotating
it so that its sample mean and covariance matrix match those of the target
dataset x2.
The rotation is based on the square root of the sample correlation matrix.
If idempotent = FALSE then this square root is based on the Cholesky
decomposition this matrix, using chol. If idempotent = TRUE the
square root is based on the spectral decomposition of this matrix, using
the output from eigen. This is a minimal rotation square root,
which means that if the input data x already have the
exactly/approximately the required summary statistics then the returned
dataset is exactly/approximately the same as the target dataset x2.
See also
anscombise modifies a dataset so that it shares sample summary
statistics with Anscombe's quartet.
Examples
### 2D examples
# The UK and a dinosaur
got_maps <- requireNamespace("maps", quietly = TRUE)
got_datasauRus <- requireNamespace("datasauRus", quietly = TRUE)
if (got_maps && got_datasauRus) {
library(maps)
library(datasauRus)
dino <- datasaurus_dozen_wide[, c("dino_x", "dino_y")]
UK <- mapdata("UK")
new_UK <- mimic(UK, dino)
plot(new_UK)
}
#> Warning: package 'maps' was built under R version 4.5.2
#> Warning: package 'datasauRus' was built under R version 4.5.2
 # Trump and a dinosaur
if (got_datasauRus) {
library(datasauRus)
dino <- datasaurus_dozen_wide[, c("dino_x", "dino_y")]
new_dino <- mimic(dino, trump)
plot(new_dino)
}
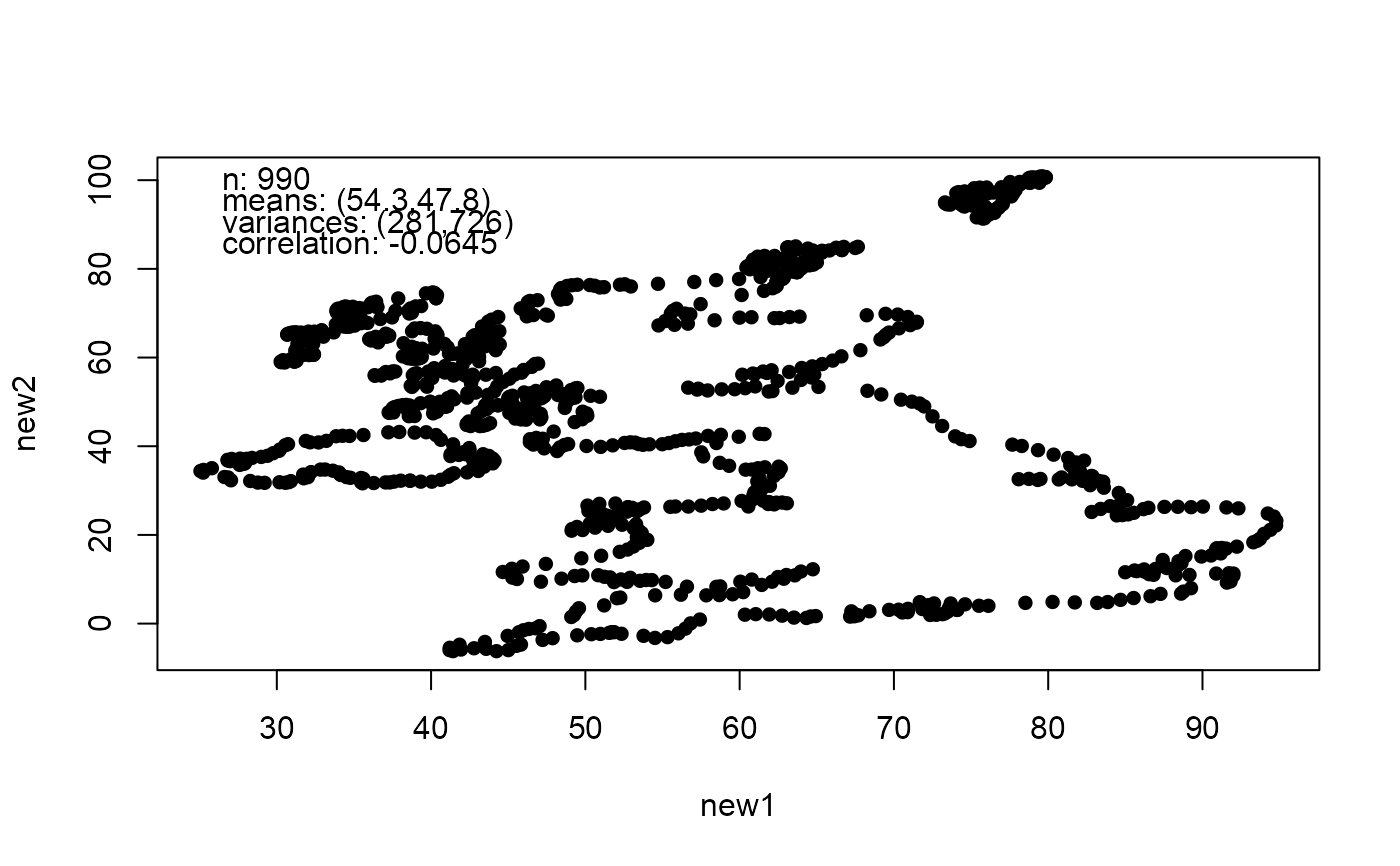
# Trump and a dinosaur
if (got_datasauRus) {
library(datasauRus)
dino <- datasaurus_dozen_wide[, c("dino_x", "dino_y")]
new_dino <- mimic(dino, trump)
plot(new_dino)
}
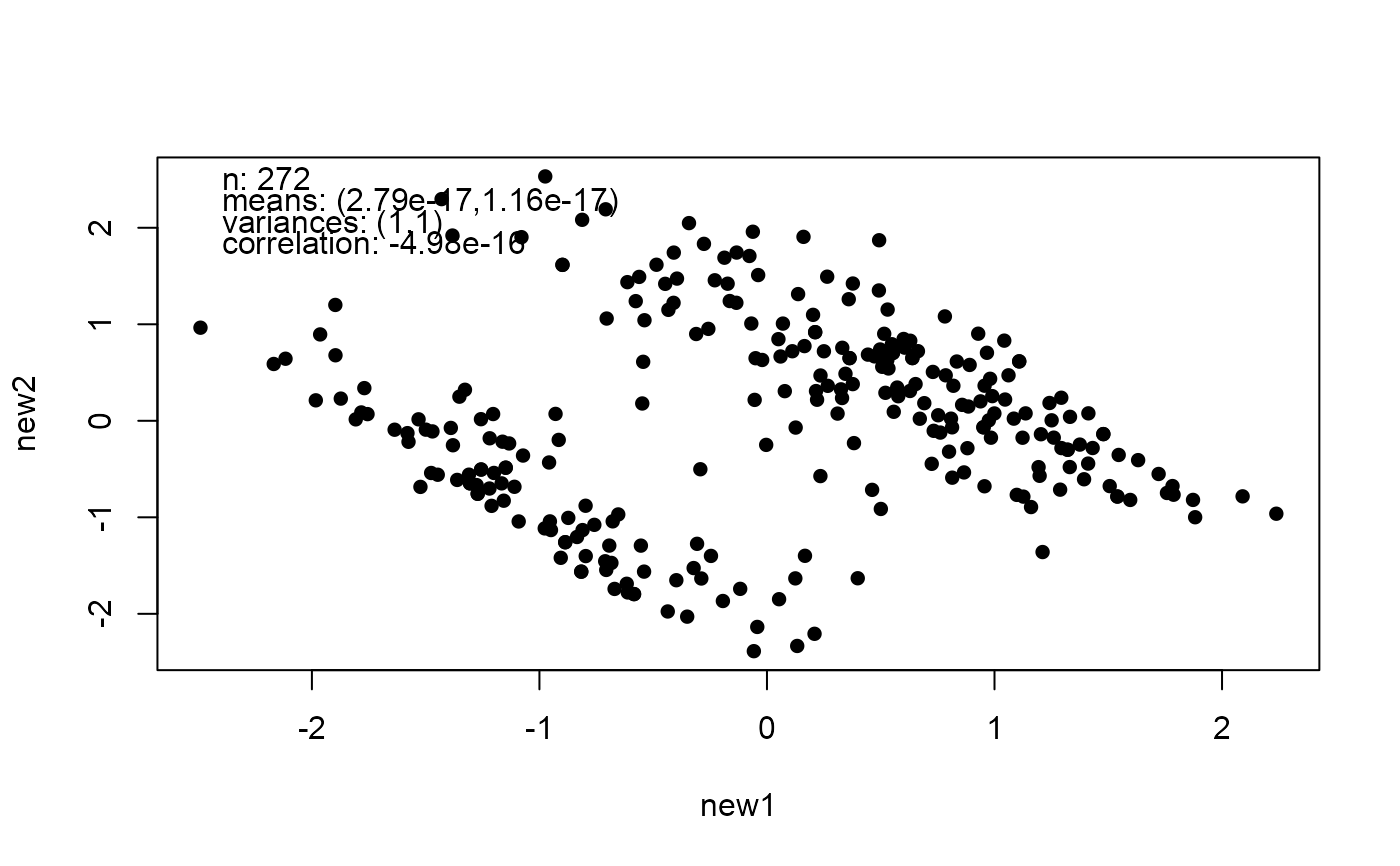
 ## Examples of passing summary statistics
# The default is zero mean, unit variance and no correlation
new_faithful <- mimic(faithful)
plot(new_faithful)
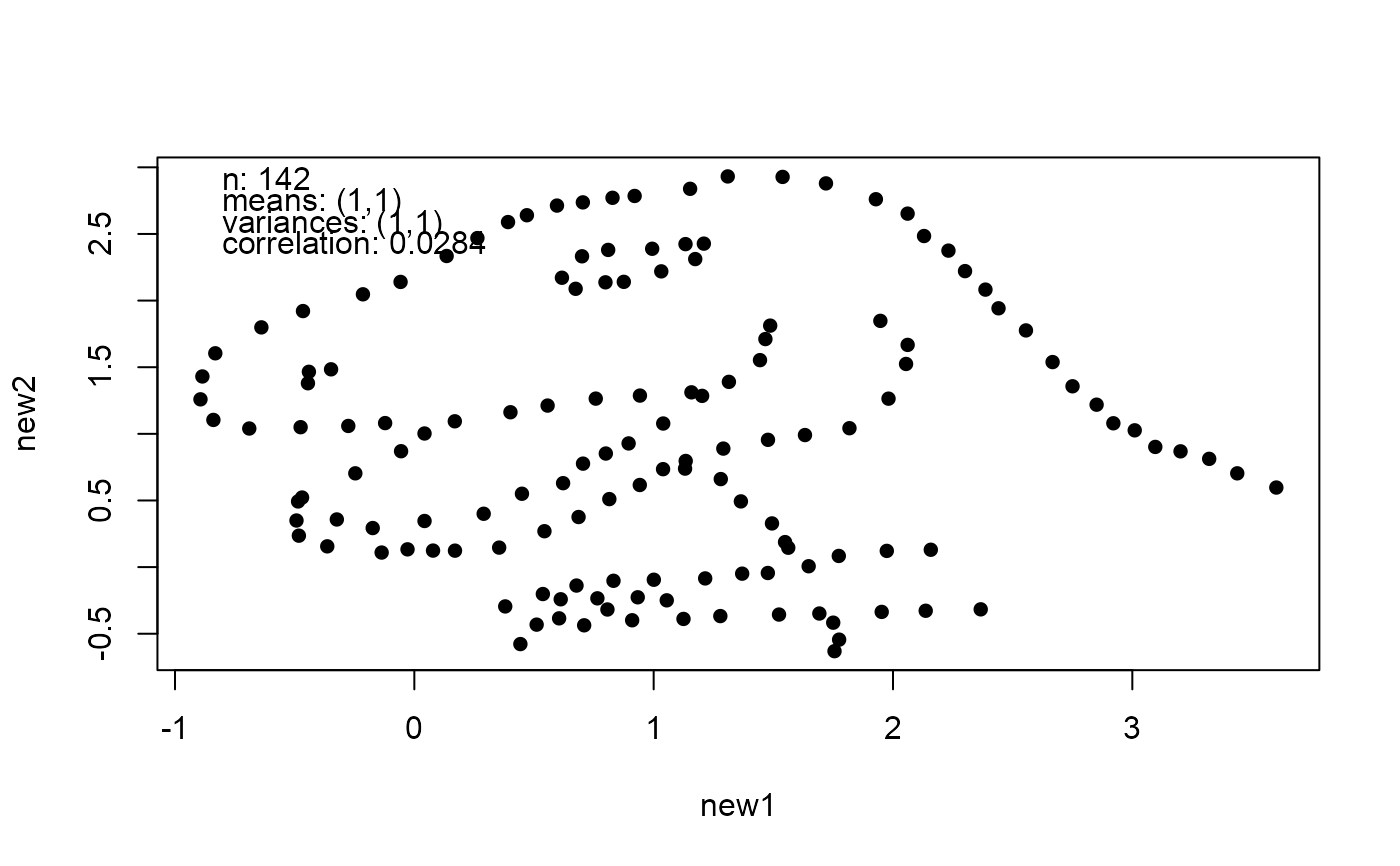
## Examples of passing summary statistics
# The default is zero mean, unit variance and no correlation
new_faithful <- mimic(faithful)
plot(new_faithful)
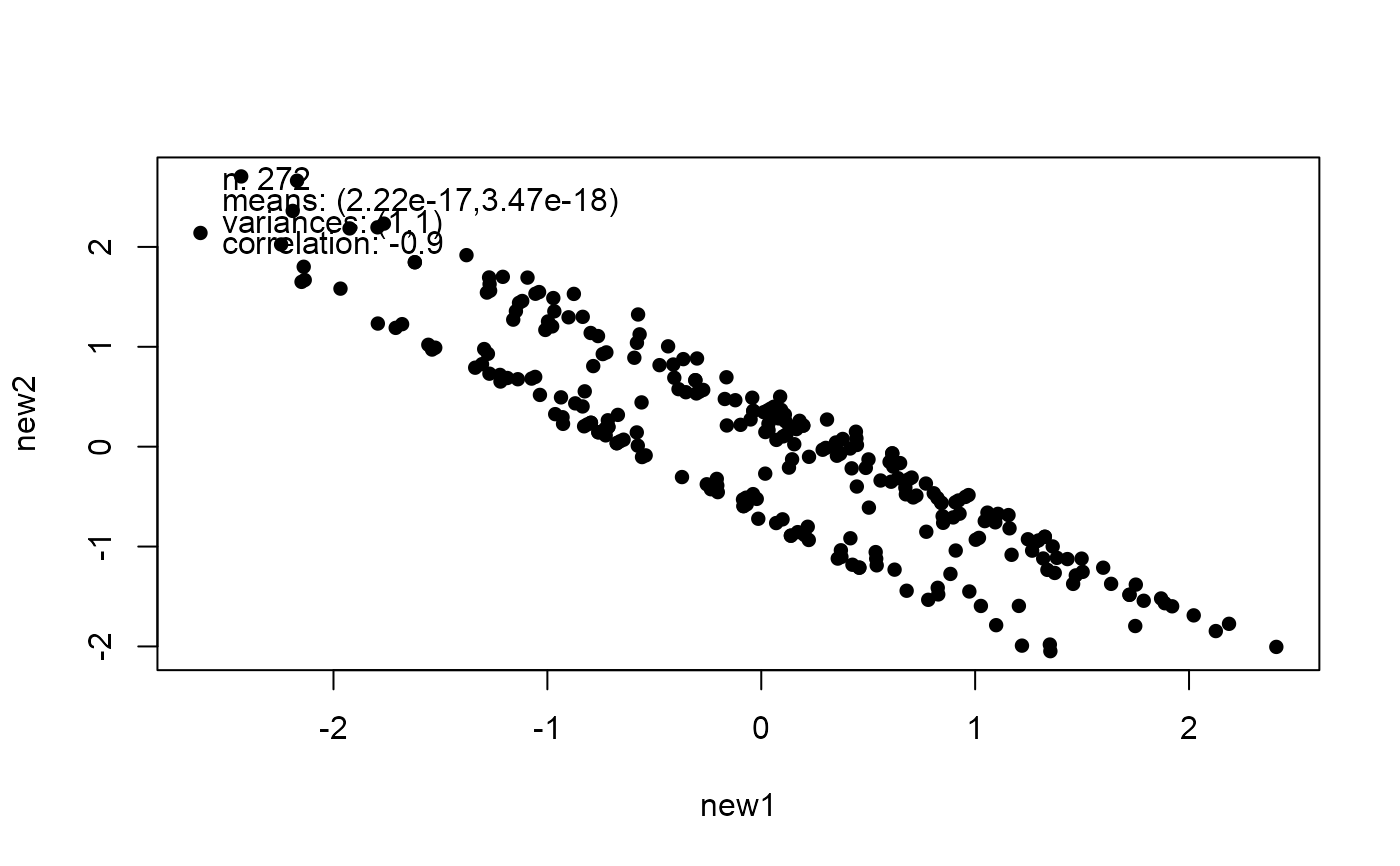
 # Change the correlation
mat <- matrix(c(1, -0.9, -0.9, 1), 2, 2)
new_faithful <- mimic(faithful, correlation = mat)
plot(new_faithful)
# Change the correlation
mat <- matrix(c(1, -0.9, -0.9, 1), 2, 2)
new_faithful <- mimic(faithful, correlation = mat)
plot(new_faithful)
 ### A 3D example
new_randu <- mimic(datasets::randu, datasets::trees)
# The samples summary statistics are equal
get_stats(new_randu)
#> $n
#> [1] 400
#>
#> $means
#> new1 new2 new3
#> 13.24839 76.00000 30.17097
#>
#> $variances
#> new1 new2 new3
#> 9.847914 40.600000 270.202796
#>
#> $correlation
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 1.0000000 0.5192801 0.9671194
#> new2 0.5192801 1.0000000 0.5982497
#> new3 0.9671194 0.5982497 1.0000000
#>
#> $intercepts
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 0.00000 0.2557471 0.1846321
#> new2 62.03131 0.0000000 0.2318999
#> new3 -36.94346 -87.1236135 0.0000000
#>
#> $slopes
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 1.000000 -6.188395 7.677857
#> new2 1.054369 1.000000 69.003356
#> new3 5.065856 1.543350 1.000000
#>
#> $rsquared
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1.0000000 0.2696518 0.9353199
#> [2,] 0.2696518 1.0000000 0.3579026
#> [3,] 0.9353199 0.3579026 1.0000000
#>
get_stats(datasets::trees)
#> $n
#> [1] 31
#>
#> $means
#> Girth Height Volume
#> 13.24839 76.00000 30.17097
#>
#> $variances
#> Girth Height Volume
#> 9.847914 40.600000 270.202796
#>
#> $correlation
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 1.0000000 0.5192801 0.9671194
#> Height 0.5192801 1.0000000 0.5982497
#> Volume 0.9671194 0.5982497 1.0000000
#>
#> $intercepts
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 0.00000 0.2557471 0.1846321
#> Height 62.03131 0.0000000 0.2318999
#> Volume -36.94346 -87.1236135 0.0000000
#>
#> $slopes
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 1.000000 -6.188395 7.677857
#> Height 1.054369 1.000000 69.003356
#> Volume 5.065856 1.543350 1.000000
#>
#> $rsquared
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1.0000000 0.2696518 0.9353199
#> [2,] 0.2696518 1.0000000 0.3579026
#> [3,] 0.9353199 0.3579026 1.0000000
#>
### A 3D example
new_randu <- mimic(datasets::randu, datasets::trees)
# The samples summary statistics are equal
get_stats(new_randu)
#> $n
#> [1] 400
#>
#> $means
#> new1 new2 new3
#> 13.24839 76.00000 30.17097
#>
#> $variances
#> new1 new2 new3
#> 9.847914 40.600000 270.202796
#>
#> $correlation
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 1.0000000 0.5192801 0.9671194
#> new2 0.5192801 1.0000000 0.5982497
#> new3 0.9671194 0.5982497 1.0000000
#>
#> $intercepts
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 0.00000 0.2557471 0.1846321
#> new2 62.03131 0.0000000 0.2318999
#> new3 -36.94346 -87.1236135 0.0000000
#>
#> $slopes
#> new1 new2 new3
#> new1 1.000000 -6.188395 7.677857
#> new2 1.054369 1.000000 69.003356
#> new3 5.065856 1.543350 1.000000
#>
#> $rsquared
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1.0000000 0.2696518 0.9353199
#> [2,] 0.2696518 1.0000000 0.3579026
#> [3,] 0.9353199 0.3579026 1.0000000
#>
get_stats(datasets::trees)
#> $n
#> [1] 31
#>
#> $means
#> Girth Height Volume
#> 13.24839 76.00000 30.17097
#>
#> $variances
#> Girth Height Volume
#> 9.847914 40.600000 270.202796
#>
#> $correlation
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 1.0000000 0.5192801 0.9671194
#> Height 0.5192801 1.0000000 0.5982497
#> Volume 0.9671194 0.5982497 1.0000000
#>
#> $intercepts
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 0.00000 0.2557471 0.1846321
#> Height 62.03131 0.0000000 0.2318999
#> Volume -36.94346 -87.1236135 0.0000000
#>
#> $slopes
#> Girth Height Volume
#> Girth 1.000000 -6.188395 7.677857
#> Height 1.054369 1.000000 69.003356
#> Volume 5.065856 1.543350 1.000000
#>
#> $rsquared
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] 1.0000000 0.2696518 0.9353199
#> [2,] 0.2696518 1.0000000 0.3579026
#> [3,] 0.9353199 0.3579026 1.0000000
#>