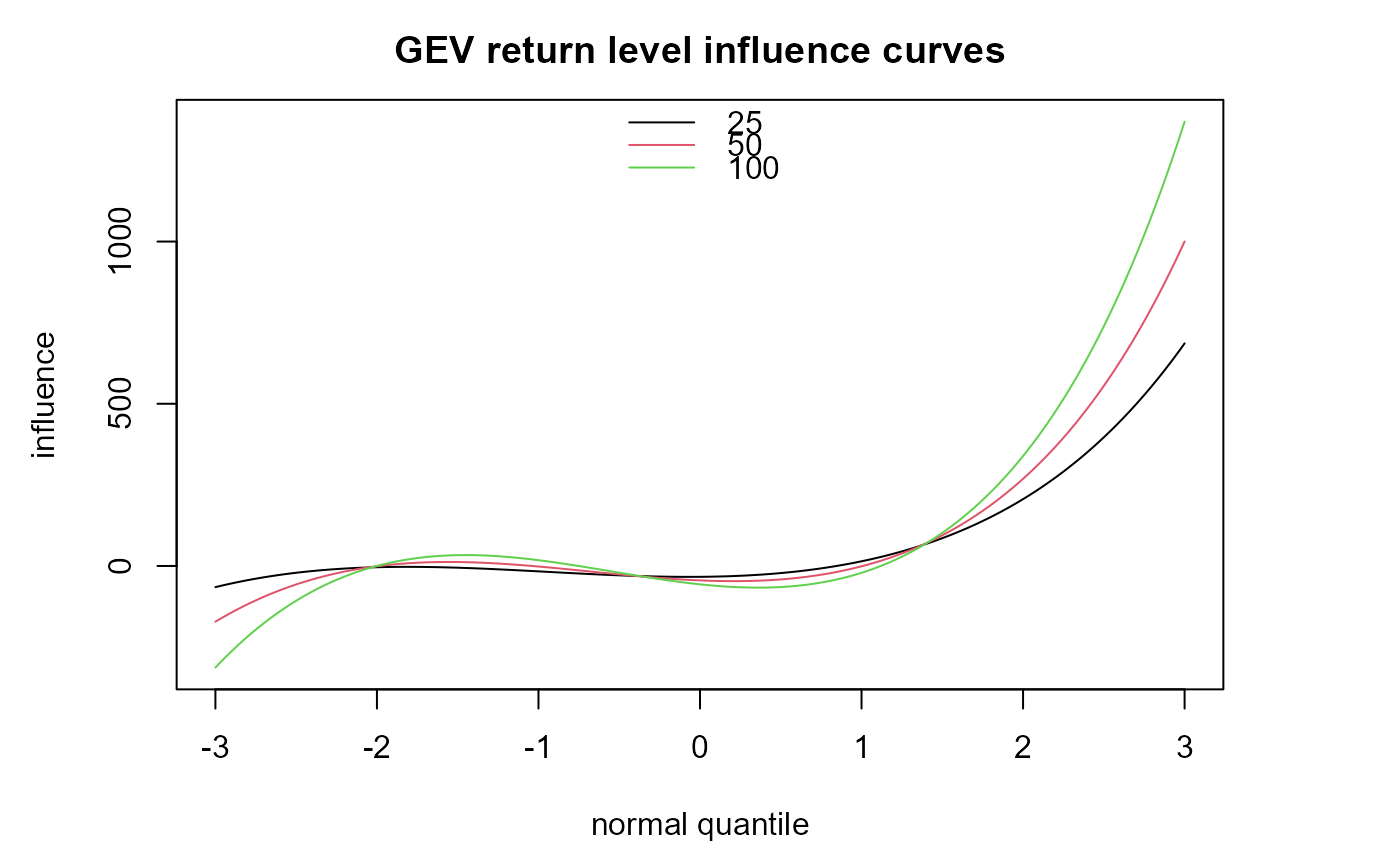
Calculates influence function curves for maximum likelihood estimators of 3 return levels based on Generalised Extreme Value (GEV) parameters.
Arguments
- z
A numeric vector. Values of normal quantiles \(z\) at which to calculate the GEV influence function. See Details.
- mu, sigma, xi
Numeric scalars supplying the values of the GEV parameters \(\mu\), \(\sigma\) and \(\xi\).
- m
A numeric vector of length 3 containing 3 unique return periods in years. All entries in
mmust be greater than 1.- npy
A numeric scalar. The number \(n_{py}\) of block maxima per year. If the blocks are of length 1 year then
npy = 1.- x
An object inheriting from class
"gev_influence_rl", returned from a call togev_influence_rl.- xvar
A logical scalar. If
xvar = "z"then the influence curves are plotted against the standard normal quantiles inx[, "z"]. Ifxvar = "y"then the influence curves are plotted against the corresponding GEV quantiles inx[, "y"].- vlines
A numeric vector. If
vlinesis supplied then black dashed vertical lines are added to the plot at the values invlineson the horizontal axis. This might be used to indicate the values of certain observations in a dataset.- ...
For
plot.gev_influence_rl: to pass graphical parameters to the graphical functionsmatplotandlegend. The parameterscol, ltyandlwdcan be used to control line colour, type and width, with the return levels in the order that they were supplied inm.
Value
gev_influence_rl: an object with class
c("gev_influence_rl", "matrix", "array"), a length(z) by 5 numeric
matrix. The first two columns contain the input values in z and the
corresponding values of y. Columns 3-5 contain the values of the GEV
influence function for the return levels in m respectively at the values
of z.
plot.gev_influence_rl: a list of the graphical parameters used in producing
the plot, either the defaults or supplied via ..., is returned
invisibly.
Details
See gev_influence for information about influence functions in
general and influence curves for the parameters of a GEV distribution in
particular. The GEV influence curves are reparameterised from
\((\mu, \sigma, \xi)\) to the required return levels.
References
Hampel, F. R., Ronchetti, E. M., Rousseeuw, P. J., and Stahel, W. A. (2005). Robust Statistics. Wiley-Interscience, New York. doi:10.1002/9781118186435
Davison, A. C. and Smith, R. L. (1990). Models for exceedances over high thresholds. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 52(3):393–425. doi:10.1111/j.2517-6161.1990.tb01796.x