Confidence intervals for the extremal index \(\theta\) for "spm" objects
Source: R/confidence_intervals.R
spm_confint.Rdconfint method for objects of class c("spm", "exdex").
Computes confidence intervals for \(\theta\) based on an object returned
from spm. Two types of interval may be returned:
(a) intervals that are based on approximate large-sample normality of the
estimators of \(\theta\) (or of \(\log\theta\) if
conf_scale = "log"), and which are symmetric about the respective
point estimates, and (b) likelihood-based intervals based on an adjustment
of a naive (pseudo-) loglikelihood, using the
adjust_loglik function in the
chandwich package. The plot method plots the
log-likelihood for \(\theta\), with the required confidence interval(s)
indicated on the plot.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'spm'
confint(
object,
parm = "theta",
level = 0.95,
maxima = c("sliding", "disjoint"),
interval_type = c("norm", "lik", "both"),
conf_scale = c("theta", "log"),
constrain = TRUE,
bias_adjust = TRUE,
type = c("vertical", "cholesky", "spectral", "none"),
...
)
# S3 method for class 'confint_spm'
plot(x, estimator = "all", ndec = 2, ...)
# S3 method for class 'confint_spm'
print(x, ...)Arguments
- object
An object of class
c("spm", "exdex"), returned byspm.- parm
Specifies which parameter is to be given a confidence interval. Here there is only one option: the extremal index \(\theta\).
- level
A numeric scalar in (0, 1). The confidence level required.
- maxima
A character scalar specifying whether to estimate confidence intervals based on sliding maxima or disjoint maxima.
- interval_type
A character scalar:
"norm"for intervals of type (a),"lik"for intervals of type (b).- conf_scale
A character scalar. If
interval_type = "norm"thenconf_scaledetermines the scale on which we use approximate large-sample normality of the estimators to estimate confidence intervals of type (a).If
conf_scale = "theta"then confidence intervals are estimated for \(\theta\) directly. Ifconf_scale = "log"then confidence intervals are first estimated for \(\log\theta\) and then transformed back to the \(\theta\)-scale.Any bias-adjustment requested in the original call to
spm, using it'sbias_adjustargument, is automatically applied here.- constrain
A logical scalar. If
constrain = TRUEthen any confidence limits that are greater than 1 are set to 1, that is, they are constrained to lie in (0, 1]. Otherwise, limits that are greater than 1 may be obtained. Ifconstrain = TRUEthen any lower confidence limits that are less than 0 are set to 0.- bias_adjust
A logical scalar. If
bias_adjust = TRUEthen, if appropriate, bias-adjustment is also applied to the loglikelihood before it is adjusted usingadjust_loglik. This is performed only if, in the call tospm,bias_adjust = "BB3"or"BB1"was specified, that is, we haveobject$bias_adjust = "BB3"or"BB1". In these cases the relevant component ofobject$bias_slorobject$bias_djis used to scale \(\theta\) so that the location of the maximum of the loglikelihood lies at the bias-adjusted estimate of \(\theta\).If
bias_adjust = FALSEorobject$bias_adjust = "none"or"N"then no bias-adjustment of the intervals is performed. In the latter case this is because the bias-adjustment is applied in the creation of the data inobject$N2015_dataandobject$BB2018_data, on which the naive likelihood is based.- type
A character scalar. The argument
typeto be passed toconf_intervalsin thechandwichpackage in order to estimate the likelihood-based intervals. Usingtype = "none"is not advised because then the intervals are based on naive estimated standard errors. In particular, if (the default)sliding = TRUEwas used in the call tospmthen the unadjusted likelihood-based confidence intervals provide vast underestimates of uncertainty.- ...
Additional optional arguments to be passed to
print.default- x
an object of class
c("confint_spm", "exdex"), a result of a call toconfint.spm.- estimator
A character vector specifying which of the three variants of the semiparametric maxima estimator to include in the plot:
"N2015", "BB2018"or"BB2018b". Seespmfor details. Ifestimator = "all"then all three are included.- ndec
An integer scalar. The legend (if included on the plot) contains the confidence limits rounded to
ndecdecimal places.
Value
A list of class c("confint_spm", "exdex") containing the following components.
- cis
A matrix with columns giving the lower and upper confidence limits. These are labelled as (1 - level)/2 and 1 - (1 - level)/2 in % (by default 2.5% and 97.5%). The row names are a concatenation of the variant of the estimator (
N2015for Northrop (2015),BB2018for Berghaus and Bucher (2018)),BB2018bfor the modified (by subtracting1 / b) Berghaus and Bucher (2018) and the type of interval (normfor symmetric andlikfor likelihood-based).- ciN
The object returned from
conf_intervalsthat contains information about the adjusted loglikelihood for the Northrop (2015) variant of the estimator.- ciBB
The object returned from
conf_intervalsthat contains information about the adjusted loglikelihood for the Berghaus and Bucher (2018) variant of the estimator.- ciBBb
The object returned from
conf_intervalsthat contains information about the adjusted loglikelihood for the modified Berghaus and Bucher (2018) variant of the estimator.- call
The call to
spm.- object
The input
object.- maxima
The input
maxima.- theta
The relevant estimates of \(\theta\) returned from
adjust_loglik. These are equal toobject$theta_slifmaxima = "sliding",object$theta_djifmaxima = "disjoint", which provides a check that the results are correct.- level
The input
level.
plot.confint_spm: nothing is returned.
print.confint_spm: the argument x, invisibly.
Details
The likelihood-based intervals are estimated using the
adjust_loglik function in the
chandwich package, followed by a call to
conf_intervals.
This adjusts the naive (pseudo-)loglikelihood so that the curvature of
the adjust loglikelihood agrees with the estimated standard errors of
the estimators. The option type = "none" should not be used in
practice because the resulting confidence intervals will be wrong.
In particular, in the intervals based on sliding maxima will provide
vast underestimates of uncertainty.
If object$se contains NAs, because the block size b
was too small or too large in the call to spm then
confidence intervals cannot be estimated. A matrix of NAs
will be returned. See the Details section of the
spm documentation for more information.
print.confint_spm prints the matrix of confidence
intervals for \(\theta\).
References
Northrop, P. J. (2015) An efficient semiparametric maxima estimator of the extremal index. Extremes 18(4), 585-603. doi:10.1007/s10687-015-0221-5
Berghaus, B., Bucher, A. (2018) Weak convergence of a pseudo maximum likelihood estimator for the extremal index. Ann. Statist. 46(5), 2307-2335. doi:10.1214/17-AOS1621
See also
spm for estimation of the extremal index
\(\theta\) using a semiparametric maxima method.
Examples
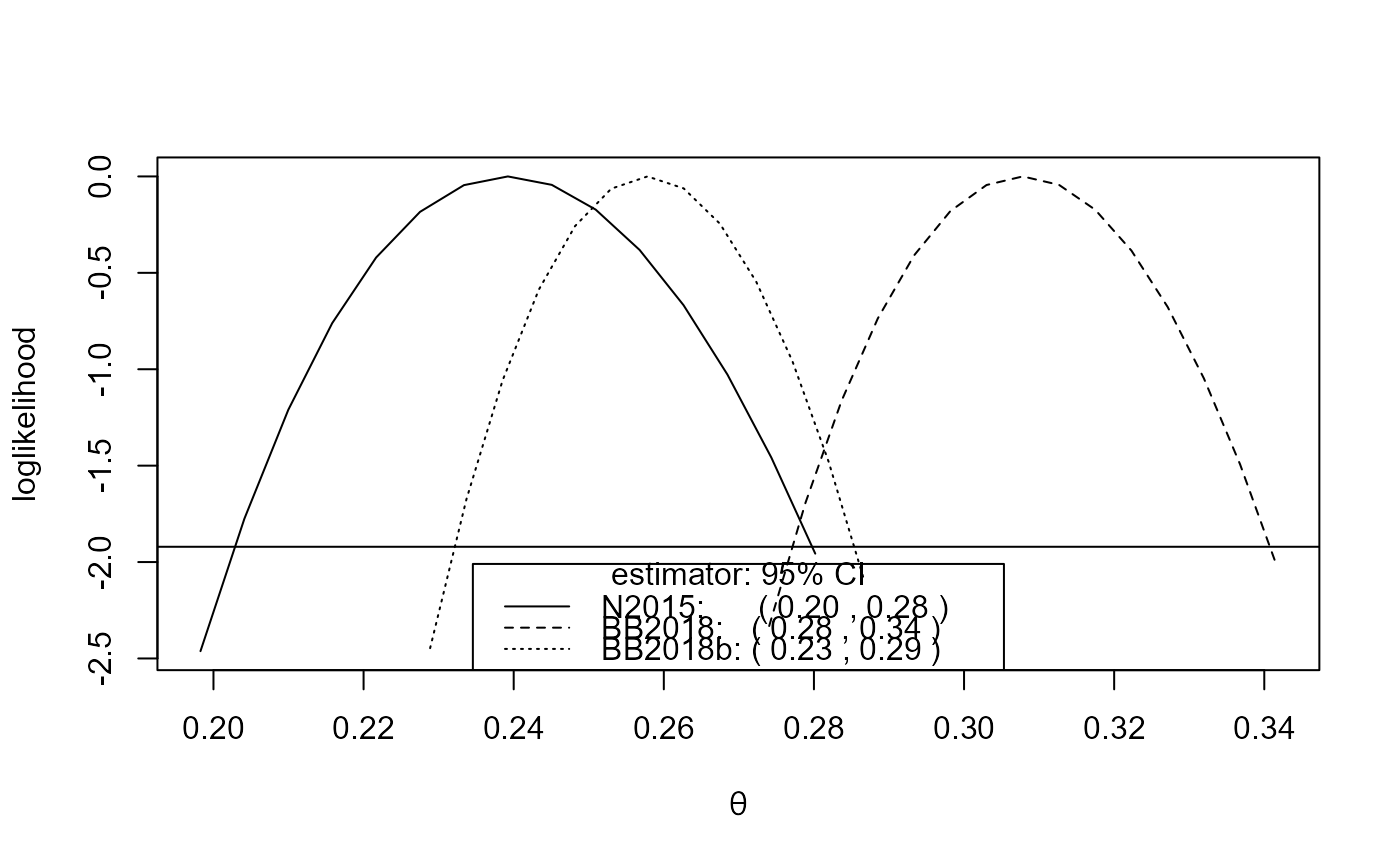
# Newlyn sea surges
theta <- spm(newlyn, 20)
confint(theta)
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015norm 0.2002191 0.2782277
#> BB2018norm 0.2756477 0.3399961
#> BB2018bnorm 0.2256477 0.2899961
cis <- confint(theta, interval_type = "lik")
cis
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015lik 0.2028802 0.2797593
#> BB2018lik 0.2771474 0.3407445
#> BB2018blik 0.2321583 0.2853566
plot(cis)
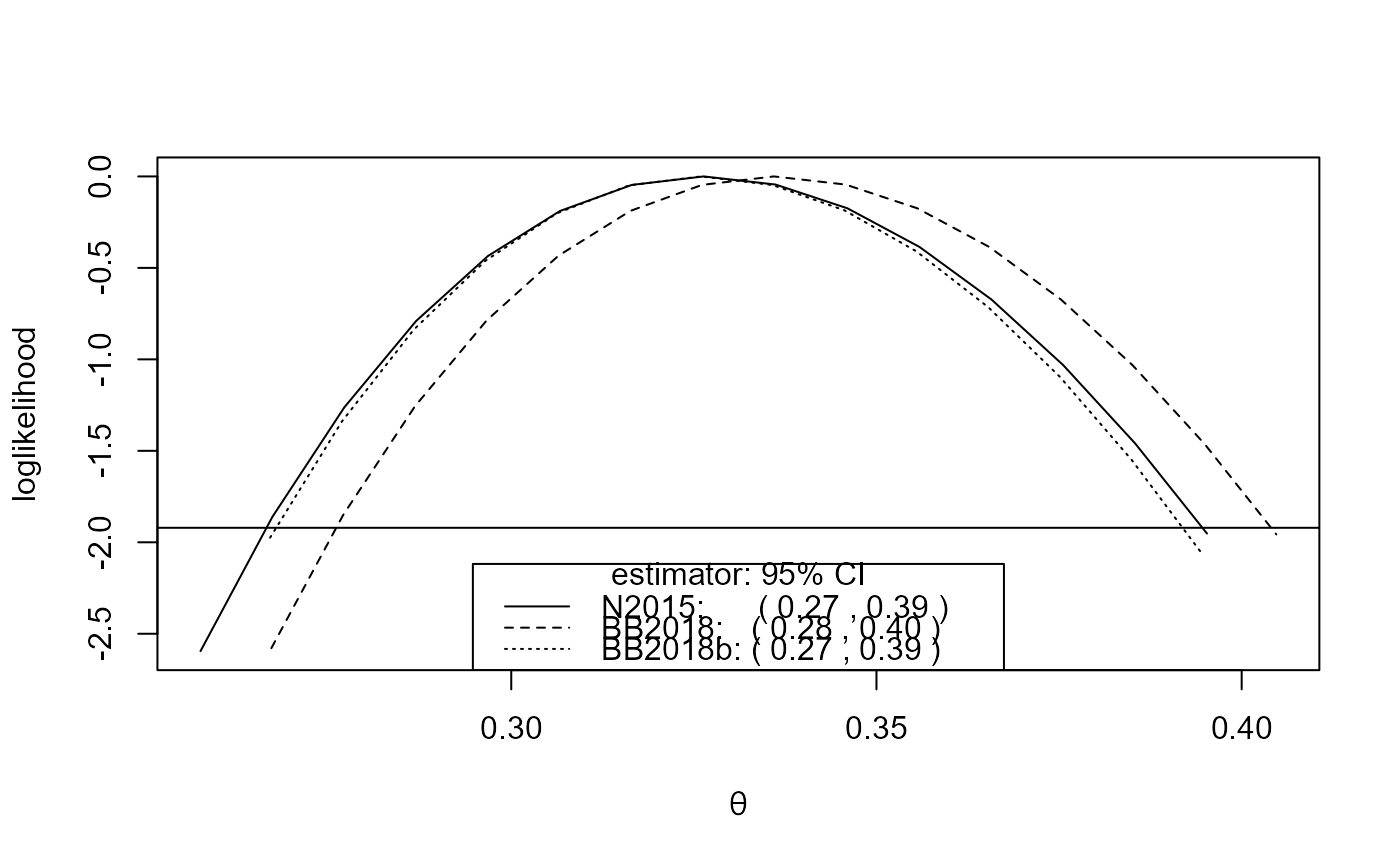
 # S&P 500 index
theta <- spm(sp500, 100)
confint(theta)
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015norm 0.2607322 0.3919727
#> BB2018norm 0.2704307 0.4014686
#> BB2018bnorm 0.2604307 0.3914686
cis <- confint(theta, interval_type = "lik")
cis
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015lik 0.2664968 0.3946247
#> BB2018lik 0.2760426 0.4040249
#> BB2018blik 0.2678191 0.3919123
plot(cis)
# S&P 500 index
theta <- spm(sp500, 100)
confint(theta)
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015norm 0.2607322 0.3919727
#> BB2018norm 0.2704307 0.4014686
#> BB2018bnorm 0.2604307 0.3914686
cis <- confint(theta, interval_type = "lik")
cis
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> N2015lik 0.2664968 0.3946247
#> BB2018lik 0.2760426 0.4040249
#> BB2018blik 0.2678191 0.3919123
plot(cis)